Why Traversing?
Traversing can be helpful when you need to visit each node of a structure. For instance, if you want to find the sum of all nodes of the tree.
Linear data structures like stacks and queues have only one way to traverse i.e. linear but hierarchical data structures like trees can be traversed in different ways. If you are looking for C++ Homework Help then you can contact codingzap.com
Tree Traversal In C
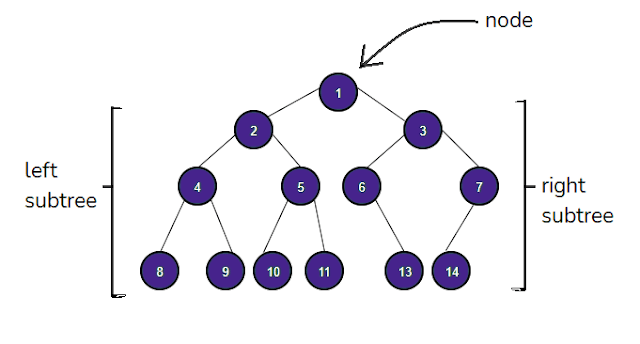
A node of a tree can be implemented in C as:
- Data
- Left Subtree
- Right Subtree
Trees can be traversed in three ways:
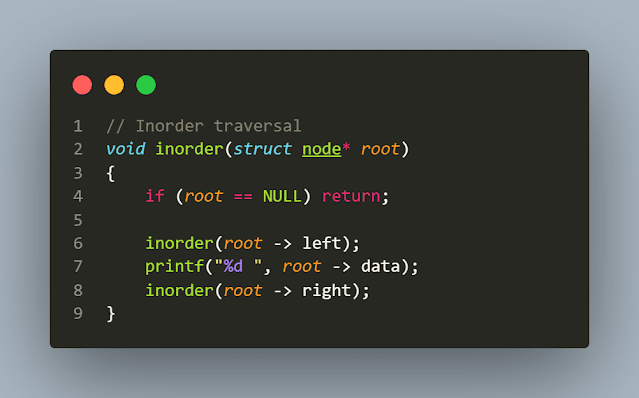
1. Inorder Traversal
Algorithm
- Visit all nodes in the left subtree
- Visit root node
- Visit all nodes in the right subtree
C Implementation
2. Preorder Traversal
Algorithm
- Visit root node
- Visit all nodes in the left subtree
- Visit all nodes in the right subtree
C Implementation
3. Postorder Traversal
Algorithm
- Visit all nodes in the left subtree
- Visit all nodes in the right subtree
- Visit root node
C Implementation
1. Creating a Node
Create a new node with left and right subtree null and data as given.
2. Insert Nodes to the Root
Create a new node and insert it to the left or right of the root
2.1 Insert Nodes to Left and Right
3. Driver Code
We are creating this tree for traversal
Code for Tree Traversal In C
// Tree traversals in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a node of tree
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Create a New Node
struct node* createNode(int data)
{
// Allocate memory eauivalent to node structure and hold
// address in node pointer
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode -> data = data;
newNode -> left = NULL;
newNode -> right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Insert a new node to left of the given node
struct node* insertLeft(struct node* root, int data)
{
root -> left = createNode(data);
return root;
}
// Insert a new node to right of the given node
struct node* insertRight(struct node* root, int data)
{
root -> right = createNode(data);
return root;
}
// Inorder traversal
void inorder(struct node* root)
{
if (root == NULL) return;
inorder(root -> left);
printf("%d ", root -> data);
inorder(root -> right);
}
// Preorder traversal
void preorder(struct node* root)
{
if (root == NULL) return;
printf("%d ", root -> data);
preorder(root -> left);
preorder(root -> right);
}
// Postorder traversal
void postorder(struct node* root)
{
if (root == NULL) return;
postorder(root -> left);
postorder(root -> right);
printf("%d ", root -> data);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct node* root = createNode(4);
insertLeft(root, 21);
insertRight(root, 13);
insertLeft(root -> left, 34);
insertRight(root -> left, 0);
insertLeft(root -> right, 18);
insertRight(root -> right, 19);
printf("Inorder traversal of the Tree is : ");
inorder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("Preorder traversal of the Tree is : ");
preorder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("Postorder traversal of the Tree is : ");
postorder(root);
return 0;
}



















0 Comments: